Read the full report here!
Learn more about bcANALYTICS and check out the 2016 and 2017 State of Dallas Housing Reports!
We are excited to release the third annual State of Dallas Housing report, the latest in our series of data-driven analytics reports that examine the issue of housing affordability within Dallas and present opportunities for equitable housing development.
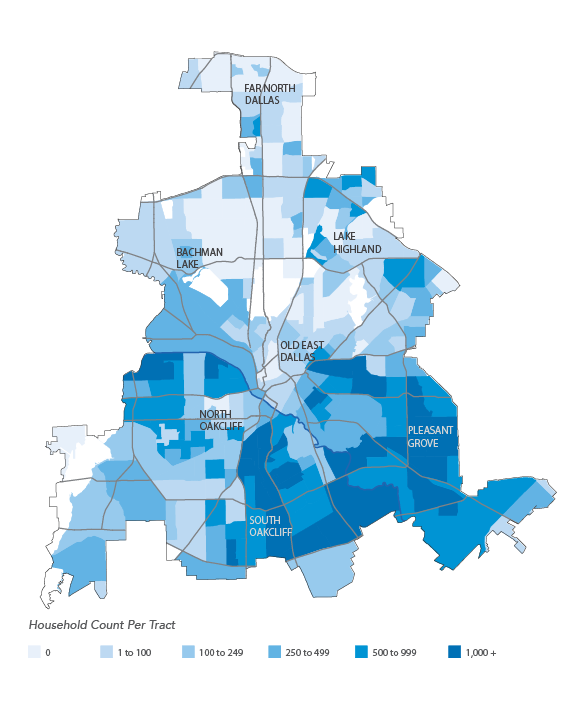
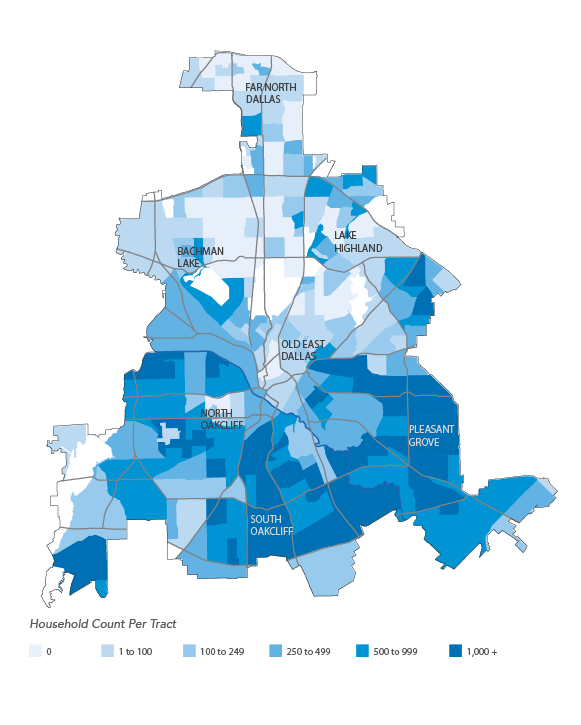
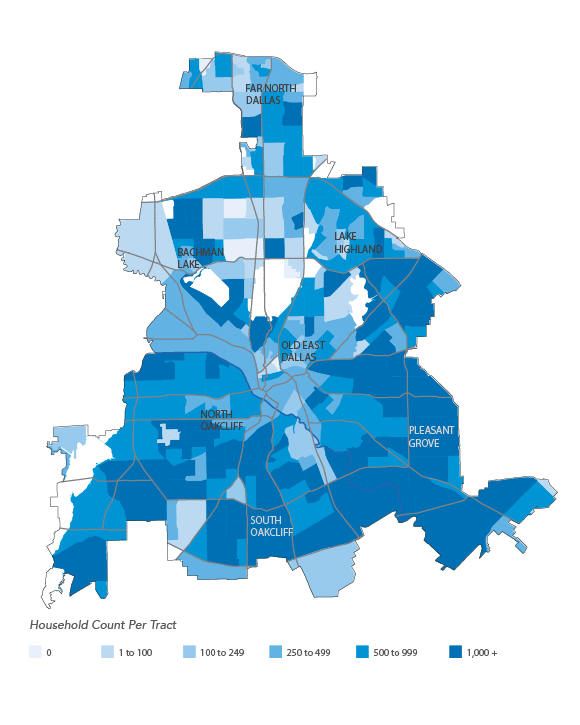
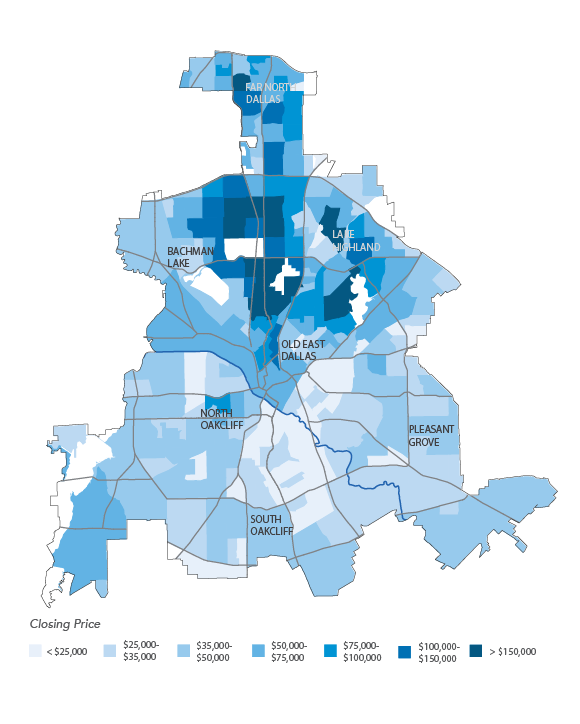
The maps and graphics included in the report illustrate longitudinal trends in housing production and new residential construction, as well as growth in population, jobs, and income, across Collin, Dallas, Denton and Tarrant counties. The report looks at median incomes by racial and ethnic group and by industry of employment in relation to average housing costs by Census tract.
The bcANALYTICS team interviewed 10 housing experts in Dallas to determine priority areas where additional research was needed. The need to better understand Dallas’s housing market within the context of the four-county region (Collin, Dallas, Denton, and Tarrant) emerged as a top priority. The report examines key data that demonstrates how Dallas’s housing market is not producing enough affordable housing to meet the needs of its socioeconomically diverse population. With costs of housing on the rise, the housing products on the Dallas market—and the regional market—are increasingly out of reach for many. Moving to surrounding communities does not, according to the study, provide a viable option for finding more affordable housing.
With the City of Dallas adopting a new Comprehensive Housing Policy, Dallas’s residents and stakeholders will need additional metrics and context to understand the issue of housing affordability at the city-wide scale. This new report aims to equip our city with the knowledge to be informed advocates for their communities’ interests.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
In 2017 North Texas continued to be one of the fastest growing regions in the United States, and one of the top housing markets in the United States. As the City of Dallas’ prepares to implement its recently passed housing policy, aimed at increasing the production of housing units across the city, it is important to understand housing production at a larger scale to pinpoint where new housing units or typologies may be needed at this critical juncture. The 2018 State of Dallas Housing Report explores current housing trends in the City of Dallas and socioeconomic trends across the four most populous counties of North Texas (Collin, Dallas, Denton, and Tarrant) to help contextualize housing production and identify potential challenges and opportunities for improving access to housing for residents of Dallas and North Texas.
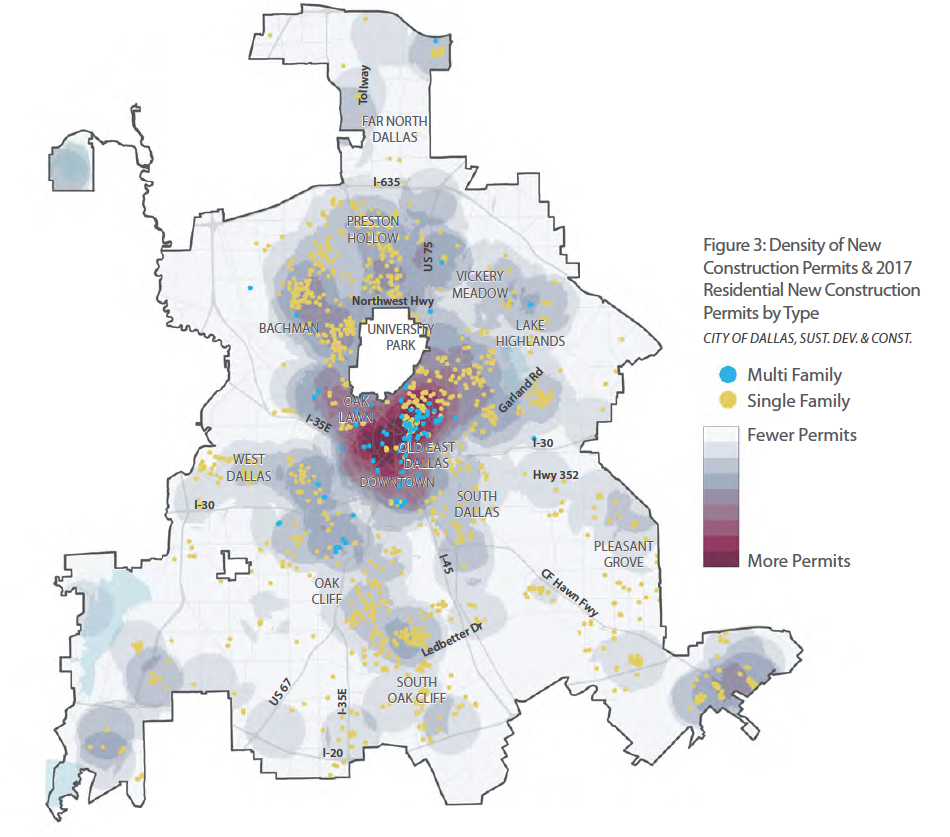
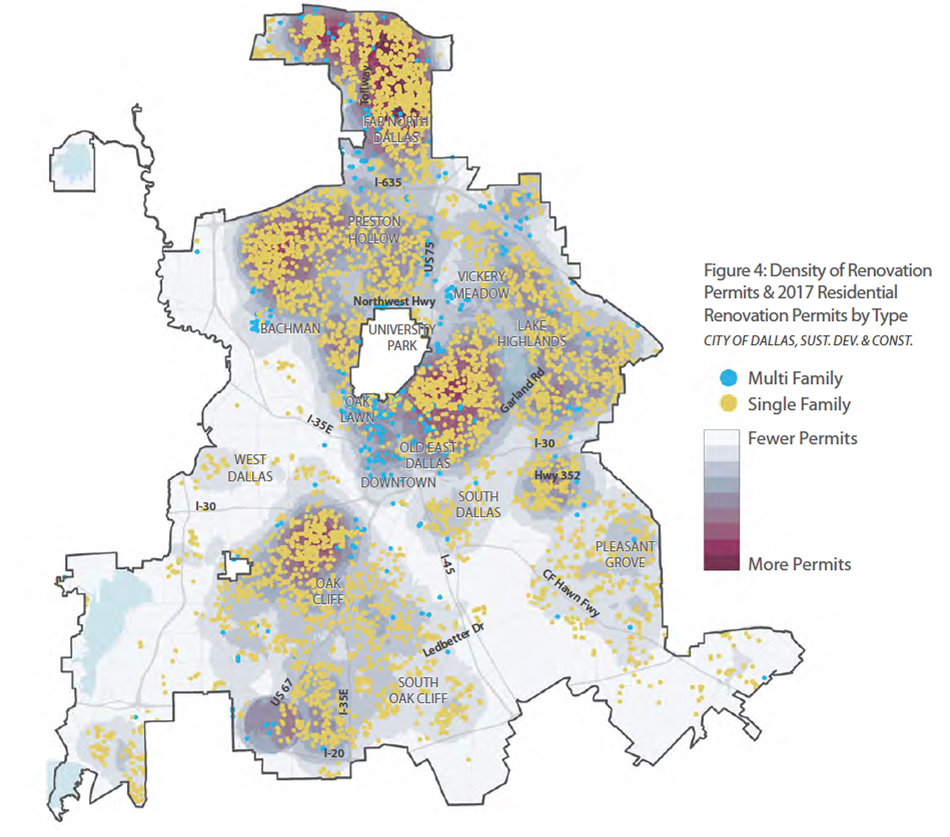
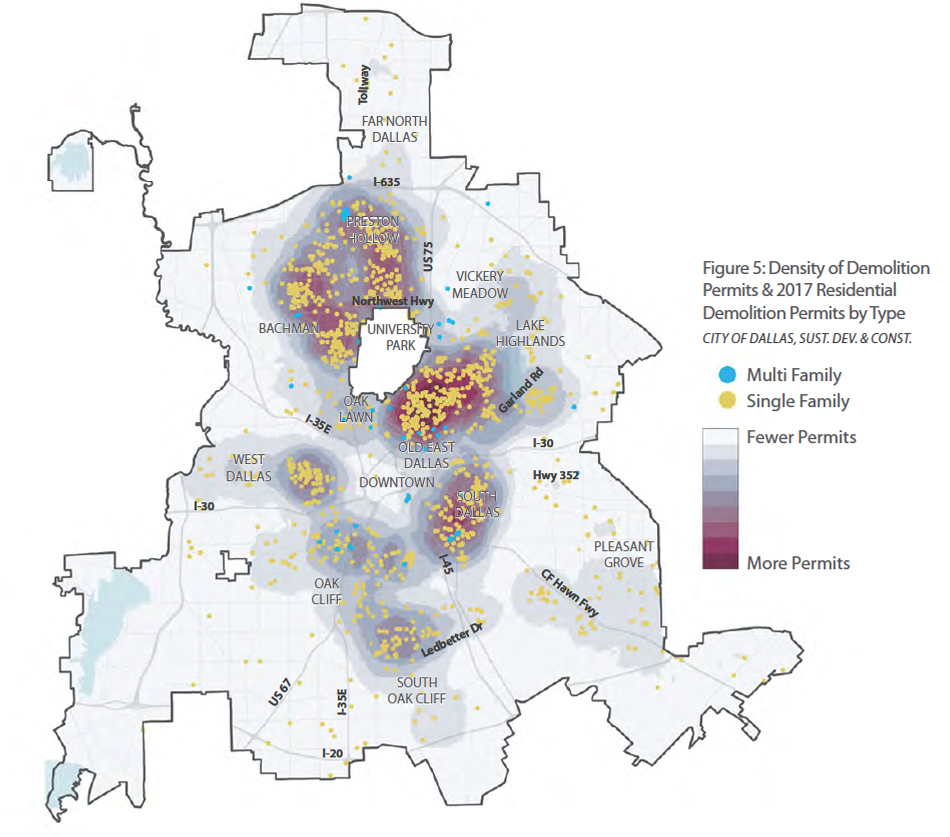
The region’s rise in population, new housing, employment, and income exemplifies the uneven nature of development and economic growth across North Texas. Growth in the region is concentrated in specific cities and neighborhoods, while other areas have experienced less measurable change in recent years. Housing production has followed this growth in parts of the region. However, housing production in the city of Dallas has been heavily concentrated in just a few of the Dallas’ nearly 400 neighborhoods despite more widespread growth across Dallas.
This report helps quantify these trends in Dallas’ housing production from 2011 to 2017, contrasting them with socioeconomic changes and housing production across North Texas. Is Dallas’ goal of increasing the production of housing feasible, inclusive, and able to address the needs of all Dallas residents? Central to this report is the focus of housing accessibility and affordability for different income and population groups in Dallas, based on the ratio of housing values to median income. Has new housing production across North Texas provided opportunities for Dallas’ median income households to access housing in surrounding communities? This report suggests the answer is no.
As more of Dallas’ housing production is focused on higher-valued homes, largely in the city’s northern sector, new housing built in North Texas from 2011 to 2016 was largely concentrated in areas that are the least affordable to Dallas’ median income households of color. As the City weighs a new housing policy to stimulate housing production in Dallas it is important to understand both the history of recent housing production in Dallas and the connection between housing production and Dallas’ existing residents.
This report finds that despite large numbers of new housing units built across the region, many Dallas households are only able to easily afford housing in certain parts of North Texas, primarily in Census tracts that are heavily segregated with high poverty and further removed from much of the economic growth in North Texas. Additionally, some of the fastest growing industries in North Texas tend to pay lower wages that create an additional barrier to accessing affordable housing in proximity to jobs and other amenities based. The lack of production of affordable rental units only further enforces the challenge of Dallas’ minority and low income residents from accessing quality affordable housing at the expense of providing luxury housing for more affluent new residents moving to neighborhoods close to Downtown Dallas.
![[bc]](http://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5248ebd5e4b0240948a6ceff/1412268209242-TTW0GOFNZPDW9PV7QFXD/bcW_square+big.jpg?format=1000w)